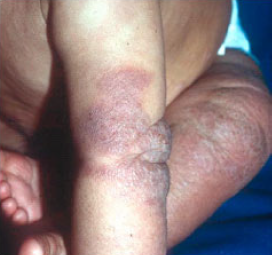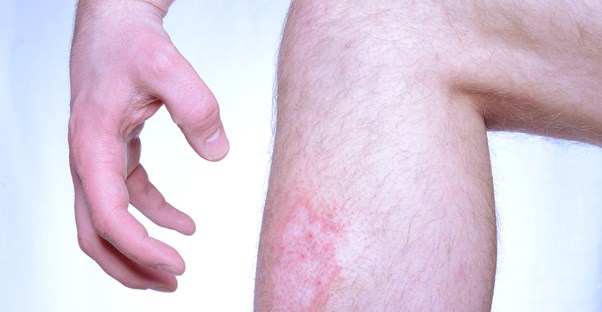
What is the best treatment for atopic dermatitis?
Treatments for atopic dermatitis Treatment can relieve your symptoms and help you live more comfortably if you are diagnosed with atopic dermatitis. Dermatologists recommend moisturizer for everyone who has atopic dermatitis. Keeping your skin well moisturized helps to prevent cracks and fissures in your skin.
How is atopic dermatitis (AD) diagnosed?
To diagnose atopic dermatitis (AD), a board-certified dermatologist carefully examines your (your child’s) skin and asks questions. To help ensure that your dermatologist has accurate information, it’s helpful to answer these questions before your appointment: Do any of your blood relatives have AD, asthma, or hay fever? What are your symptoms?
How can a treatment plan created by a dermatologist help?
A treatment plan created by a board-certified dermatologist can help: 1 Reduce flare-ups 2 Ease symptoms, such as itch and pain 3 Prevent AD from worsening 4 Decrease your risk of developing thickened skin, which tends to itch all the time 5 Keep your skin moist 6 Lower your risk of infection More ...

How can I help someone with dermatitis?
Lifestyle and home remediesMoisturize your skin. Routinely applying a moisturizer can help your skin.Use anti-inflammation and anti-itch products. ... Apply a cool wet cloth. ... Take a comfortably warm bath. ... Use medicated shampoos. ... Take a dilute bleach bath. ... Avoid rubbing and scratching. ... Choose mild laundry detergent.More items...•
What is the best treatment for patients with atopic dermatitis?
Topical corticosteroids have been the mainstay of treatment for atopic dermatitis flare-ups and are the agents to which other treatments are compared. Calcineurin inhibitors should be used as second-line agents, and, rarely, systemic therapies may be considered in adults.
How do people live with atopic dermatitis?
5 tips from an eczema patientKNOW YOUR TRIGGERS. What triggers an itching and scratching cycle for you? ... GET REGULAR EXERCISE. Do as much as you can but know when you've reached your limit. ... TRY QIGONG. ... DO SOMETHING CREATIVE. ... FEEL FREE TO EXPLORE.
What is the standard of care for atopic dermatitis?
Standard treatment modalities for the management of these patients are centered around the use of topical anti-inflammatory preparations and moisturization of the skin, but patients with severe disease may require phototherapy or systemic treatment [2,3]. Conventional therapy for atopic dermatitis is reviewed here.
How do you stop atopic dermatitis from spreading?
Atopic Dermatitis PreventionAfter a flare-up, you can do things to keep your skin healthy and make another one less likely.Avoid triggers. Figure out what causes your skin problems and try to avoid those triggers. ... Take care of your skin. ... Take shorter showers and baths. ... Use gentle soaps.
What foods to avoid if you have eczema?
Some common foods that may trigger an eczema flare-up and could be removed from a diet include:citrus fruits.dairy.eggs.gluten or wheat.soy.spices, such as vanilla, cloves, and cinnamon.tomatoes.some types of nuts.
Do and don'ts in atopic dermatitis?
DOs and DON'Ts in Managing Eczema: DO avoid triggers of the rash, including stress. DO moisturize your skin daily, even when you have no symptoms. Use an odor-free oil-based cream or ointment (not lotion), best applied just after bathing while skin is still damp. Use hypoallergenic products when possible.
Does eczema shorten lifespan?
Hospitalization due to AD flares and related infections is associated with an 8.3 year reduction in lifespan compared to the general population. Outside of hospitalization, the risk for death due to any cause is slightly increased in people with AD.
Can you be hospitalized for eczema?
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease that is generally managed on an outpatient basis. However, a significant percentage of patients may develop complications severe enough to require inpatient treatment.
Should you cover eczema or let it breathe?
Are there any possible side effects? Wet wrapping to treat moderate to severe eczema is generally well tolerated. However, there are a few potential risks and side effects to consider. Covering the skin increases the potency of topical treatments, which may make them more effective.
What foods help eczema?
Anti-inflammatory diet for eczema Anti-inflammatory diets limit dairy, whole grains, red meat, flour and sugar, but emphasize vegetables and fish. In fact, going vegan (or keeping nearly a fully plant-based diet) is also a good route to take.
Can atopic dermatitis spread?
Overview of Atopic Dermatitis Atopic dermatitis is not contagious, so it cannot be spread from person to person. Atopic dermatitis causes the skin to become extremely itchy. Scratching leads to further redness, swelling, cracking, “weeping” clear fluid, crusting, and scaling.
What is the first line therapy in atopic dermatitis ad?
Use of topical corticosteroids is the first-line treatment for atopic dermatitis flare-ups. Pimecrolimus and tacrolimus are topical calcineurin inhibitors that can be used in conjunction with topical corticosteroids as first-line treatment.
Which cream is best for atopic dermatitis?
Low strength hydrocortisone creams (Cortaid, Nutracort) are available at most drugstores and grocery stores. You can apply hydrocortisone immediately after you moisturize your skin. It's most effective for treating a flare-up.
Is hydrocortisone good for atopic dermatitis?
Topical corticosteroids have been the mainstay of treatment for atopic dermatitis over the past 40 years. Hydrocortisone was the first to be used; some 30 additional corticosteroid compounds have now been licensed for treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Which of the below was approved for treatment of atopic dermatitis?
Crisaborole topical ointment 2% (Eucrisa) was approved by the FDA in December 2016 for mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in adults and children aged 2 years or older. The approval was based on two placebo-controlled trials (n=1522).
How to treat ad dermatitis?
Lower your risk of infection. While a dermatologist tailors each AD treatment plan to a patient’s individual needs, most treatment plans include the following: Skin care: A skin care plan for AD involves: Bathing.
What are the changes dermatologists recommend?
You’ll find the changes that dermatologists recommend at: Atopic dermatitis: Self-care. Image.
What is the best treatment for AD?
Some people need stronger treatment for their AD. For these patients, a dermatologist may prescribe phototherapy or a medication that works throughout the body. Phototherapy: This is another word for light treatments that can safely and effectively treat AD, even in children.
How to treat a skin infection?
To treat an infection, you may need to apply a medication to your skin or take medication.
How does phototherapy work?
Phototherapy works by exposing your skin to ultraviolet (UV) light. It’s given at a dermatologist’s office, hospital, or phototherapy treatment center. For phototherapy to be effective, you will need 2 to 3 treatments per week for the amount of time prescribed by your dermatologist.
What is the best treatment for a swollen face?
When this is part of your treatment plan, you may apply one or more of the following: A corticosteroid. Crisaborole ointment. Pimecrolimus cream or tacrolimus ointment. Coal tar. Applying medication to your skin as directed can improve your skin’s ability to keep out germs and everyday substances that can irritate it.
What is systemic treatment for eczema?
Also called “systemic treatment,” this medication works on the immune system and can bring tremendous relief. To learn more about this type of treatment, go to: When your child needs strong medicine to control eczema.
Local, state and federal government programs
Medicare’s Prescription Drug Program can provide extra help with the cost of prescription drugs if you qualify and are a Medicare beneficiary.
Non-profit programs
The PAN Foundation helps people with chronic diseases including atopic dermatitis, pay for prescriptions
Drug maker patient assistance programs (PAPs)
PAPs are set-up by drug companies to offer free or low-cost drugs to those who cannot afford their medication. Companies offer these programs voluntarily, meaning the government does not require them to provide free medicine. As a result, each program has its own rules.