
How is atrial fibrillation (AF) treated?
The treatment for atrial fibrillation (AF) either controls the heart rate or changes the rhythm back to normal. Because of the risk of blood clots forming and causing a stroke, the treatment always, except in people at very low risk, includes medication to prevent blood clots (anticoagulation).
What is atrial fibrillation (AFIB)?
Atrial fibrillation (also called AFib or AF) is a quivering or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications. At least 2.7 million Americans are living with AFib. Dealing with AFib can be overwhelming.
Is there an online community for people living with atrial fibrillation?
If you or someone you love is affected by atrial fibrillation, explore our online community for people living with AFib. My AFib Experience Webinar - Is there more you can do for your AFib patients?
What is the American Heart Association's policy on atrial fibrillation?
The American Heart Association maintains strict policies preventing supporters from influencing science-based health information. A list of supporters can be found here. Atrial Fibrillation What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Is there an atrial fibrillation support group?
Atrial Fibrillation Support Group Emory Heart & Vascular Center now offers a support group for all patients with atrial fibrillation (AF or A-Fib) and their family members.
What to do if a patient is in AFib?
How to help: Call a doctor. AFib episodes rarely cause serious problems, but they'll need to get checked out. If they're uncomfortable or their heart is beating rapidly, call 911 or go to an emergency room. Doctors may use medications or a device called a cardioverter to help their heart go back to a normal rhythm.
What helps rapid atrial fibrillation?
Treating atrial fibrillation Treatment may involve: medicines to prevent a stroke (people with atrial fibrillation are more at risk of having a stroke) medicines to control the heart rate or rhythm. cardioversion – where the heart is given a controlled electric shock to restore normal rhythm.
Can you live well with atrial fibrillation?
Afib is not a dangerous heart rhythm. If treated well, many people with Afib lead normal lives. Afib has many causes - some are out of your control, but some CAN be changed! take a blood thinner based on your risk factors).
How long is too long to stay in AFib?
Paroxysmal Afib lasts less than one week and usually stops on its own without treatment. (Paroxysmal is pronounced par-ək-ˈsiz-məl.) Persistent Afib lasts more than one week and needs treatment. Long-standing persistent Afib lasts more than a year and is sometimes difficult to treat.
What triggers AFib attacks?
Over-the-counter cold, flu, and cough medications can trigger A-fib attacks because these medications stimulate the heart. Recreational drugs. Marijuana can stimulate the heart through raising the heart rate by a significant percent for several hours. Other drugs such as cocaine can also trigger an abnormal heartbeat.
What sleeping position is best for AFib?
A left lateral recumbent position increases the dimensions of the left atrium and the right pulmonary veins and thereby increases local myocardial stress (Wieslander et al., 2019).
What can worsen atrial fibrillation?
drinking excessive amounts of alcohol, particularly binge drinking. being overweight (read about how to lose weight) drinking lots of caffeine, such as tea, coffee or energy drinks. taking illegal drugs, particularly amphetamines or cocaine.
What heart rate is too high with AFib?
The most obvious symptom of atrial fibrillation (AF) is palpitations caused by a fast and irregular heartbeat. A normal heart rate, when you are resting, should be between 60 and 100 beats a minute. In atrial fibrillation, it may be over 140 beats a minute.
Does AFib get worse with age?
Yes. Your risk of developing atrial fibrillation, a common heart rhythm disorder, increases as you become older.
Does AFib make you sleep a lot?
This lack of blood supply can cause fatigue, even when you're resting or being only slightly active. Everyone gets tired from time to time, but the fatigue that accompanies a heart condition like Afib is often described as: Constantly tired.
Can atrial fibrillation be cured permanently?
There is no cure for persistent atrial fibrillation. But treatment can slow or prevent symptoms, making it easier for you to manage the condition. Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and drinking less alcohol can also help reduce abnormal heart rhythms and prevent complications.
Is atrial fibrillation an emergency?
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia managed by emergency and acute general physicians. There is increasing evidence that selected patients with acute atrial fibrillation can be safely managed in the emergency department without the need for hospital admission.
What is the best position to sleep if you have AFib?
A left lateral recumbent position increases the dimensions of the left atrium and the right pulmonary veins and thereby increases local myocardial stress (Wieslander et al., 2019).
How many beats per minute is AFib?
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation A normal heart rate, when you are resting, should be between 60 and 100 beats a minute. In atrial fibrillation, it may be over 140 beats a minute. If you notice an irregular heartbeat and/or have chest pain, see your doctor immediately.
What is the first drug of choice for atrial fibrillation?
Amiodarone as a first-choice drug for restoring sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation: a randomized, controlled study.
What is atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (also called AFib or AF) is a quivering or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications. At least 2.7 million Americans are living with AFib.
Connect with People Who Care
If you or someone you love is affected by Atrial Fibrillation, explore our digital community, My AFib Experience ®.
Be inspired and stay informed
Heart Insight® e-news is our trusted, award-winning monthly publication for people living with heart disease, their families and caregivers.
What is atrial fibrillation?
The heart has four chambers - two atria and two ventricles. The walls of these chambers are mainly made of special heart muscle. Normally, the contractions of your heart are controlled by a sophisticated electrical system that keeps the four chambers contracting regularly, in the correct order.
Why is it important to know about atrial fibrillation?
Even without symptoms, it's important to diagnose AF because the abnormal rhythm can cause blood clots to form in the heart. Most people with AF need to take a medicine to thin the blood to stop any blood clot from forming. If a clot does form then it may travel in the blood vessels to your brain and cause a stroke.
What is the normal heart rate for AF?
An abnormal heartbeat rhythm is called an arrhythmia. A normal heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats a minute (bpm) when you're resting. In AF the heart rate can sometimes be very fast (often between 140 and 180 bpm) as well as being irregular. Atrial Fibrillation.
How fast does the atria contract?
The atria then quiver randomly (fibrillate). This means that the atria only partially squeeze (contract) - but very rapidly (up to 400 times per minute). Only some of these impulses pass through to the ventricles and they do so in a very random and haphazard way.
What is AF in medical terms?
High blood pressure puts a strain on the heart muscle. AF is a common complication of various heart conditions. For example: AF is a complication of coronary heart disease. Coronary heart disease is the condition that causes chest pains (angina) and heart attacks and is common in older people.
How many types of AF are there?
There are three different types of AF:
Does persistent AF come back?
Persistent AF tends to come and go so it may come back again at some point after successful treatment.
What to do if you think you have atrial fibrillation?
If you think you may have atrial fibrillation, it is critical that you make an appointment with your family doctor. If atrial fibrillation is found early, your treatment may be easier and more effective. However, you may be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist).
How to diagnose atrial fibrillation?
To diagnose atrial fibrillation, your doctor may review your signs and symptoms, review your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. Your doctor may order several tests to diagnose your condition, including:
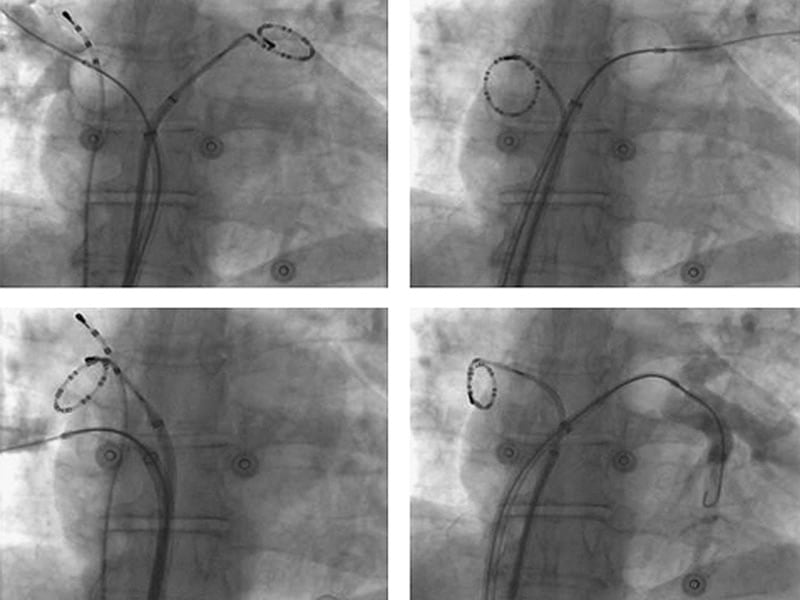
How does catheter ablation help with atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is often caused by rapidly discharging triggers, or "hot spots." In catheter ablation to treat atrial fibrillation, a doctor inserts long, thin tubes (catheters) into your groin and guides them through blood vessels to your heart. The electrodes at the tips of the catheters help your doctor determine where these triggers are located. Electrodes at the catheter tips can use radiofrequency energy, extreme cold (cryotherapy) or heat to destroy these triggers, scarring the tissue so that the erratic signals are normalized.
What is the procedure called when a catheter is placed in the left atrium?
Left atrial appendage closure. Your doctor may also consider a procedure called left atrial appendage closure. In this procedure, doctors insert a catheter through a vein in the leg and eventually guide it to the upper left heart chamber (left atrium).
What is the best medication for atrial fibrillation?
These medications include dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban. They are shorter acting than warfarin and usually don't require regular blood tests or monitoring by your doctor.
What to do if you have an irregular heartbeat?
If you have an irregular or pounding heartbeat, make an appointment with your family doctor. If atrial fibrillation is found early, treatment may be easier and more effective. You may be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist).
What is the procedure to reset the rhythm of the heart?
If A-fib symptoms are bothersome or if this is the first episode of atrial fibrillation, a doctor may attempt to reset the heart rhythm (sinus rhythm) using a procedure called cardioversion.
What is the most common test for atrial fibrillation?
The most commonly used tests to diagnose atrial fibrillation include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): The ECG draws a picture on graph paper of the electrical impulses traveling through the heart muscle. An EKG provides an electrical “snapshot” of the heart.
Where does atrial fibrillation occur?
Because atrial fibrillation usually begins in the pulmonary veins or at their attachment to the left atrium, energy is applied around the connections of the pulmonary veins to the left atrium during the pulmonary vein ablation procedure.
What is electrical cardioversion?
Electrical Cardioversion: A cardioversion electrically “resets” the heart. Medications alone are not always effective in converting atrial fibrillation to a more normal rhythm. Sometimes cardioversion is used to restore a normal heart rhythm and allow the medication to successfully maintain the normal rhythm.
What is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria?
Atrial fibrillation ( AF or AFib) is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria. Instead of the SA node (sinus node) directing the electrical rhythm, many different impulses rapidly fire at once, causing a very fast, chaotic rhythm in the atria.
What is the rate of impulses in the atria?
The ventricles contract irregularly, leading to a rapid and irregular heartbeat. The rate of impulses in the atria can range from 300 to 600 beats per minute. There are two types of atrial fibrillation. Paroxysmal is intermittent, meaning it comes and goes and continuous is persistent.
What is an ECG recording of atrial fibrillation?
An ECG recording of atrial fibrillation. Instead of the impulse traveling in an orderly fashion through the heart, many impulses begin at the same time and spread through the atria, competing for a chance to travel through the AV node.
Why is AV node ablation used?
Because the patient will continue to have atrial fibrillation, an anticoagulant medication is prescribed to reduce the risk of stroke. Important note: Due to better treatment alternatives, AV node ablation is rarely used to treat atrial fibrillation.
Connect with People Who Care
If you or someone you love is affected by atrial fibrillation, explore our online community for people living with AFib.
Guidelines and Research
Written by American Heart Association editorial staff and reviewed by science and medicine advisers. See our editorial policies and staff.
What is the treatment for abnormal heart rate?
Once your heart rate is under control, the next management consideration is usually treating the abnormal heart rhythm with medications to restore the heart rhythm to normal (also known as chemical/pharmacological cardioversion). Significant side effects may occur, and your healthcare provider will most likely want to monitor progress closely.
What is the purpose of AF medication?
Medications for atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) Medications are often prescribed to prevent and treat blood clots which can lead to a stroke. Additional drugs may be prescribed to control heart rate and rhythm in the AFib patient. These medications may also be used in conjunction with other treatments. The heart rhythm can be more difficult ...
What to do if you forget to take anticoagulant?
If you forget to take your daily anticoagulant dose, don't take an extra one to catch up! Follow your healthcare provider's directions about what to do if you miss a dose. Always talk to your healthcare provider about switching from one anticoagulant to another (including changing to a generic version).
What is the best way to slow down the heart's rhythm?
Sodium channel blockers which help the heart's rhythm by slowing the heart's ability to conduct electricity. Examples may include: Flecainide (Tambocor®) Propafenone (Rythmol®) Quinidine (Various) Potassium channel blockers help the heart’s rhythm by slowing down the electrical signals that cause AFib.
What is StopAfib.org?
StopAfib.org was created for patients by patients to provide accurate information and genuine support for those affected by atrial fibrillation. Explore our online community and connect with other patients, families, and caregivers.
Is StopAfib affiliated with the American Heart Association?
StopAfib.org is a division of the American Foundation for Women's Health. Neither is affiliated with the American Heart Association, though we collaborate with the American Heart Association on various projects.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment